

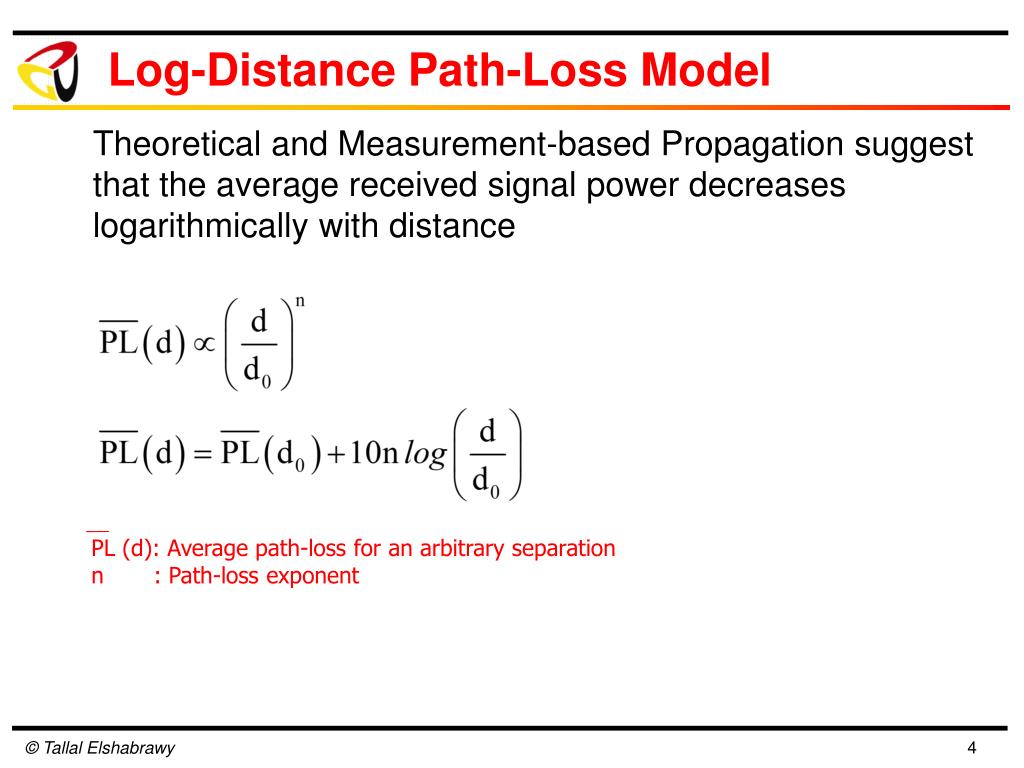
WLAN based communications also fall into this category.Path loss of radio transmitted through air or vacuum On the other side, commercial AM radio broadcasting doesn’t essentially require line-of-sight communications. This path loss model (also termed free space path loss model) becomes more relatable to line-of-sight or near line-of-sight communications such as microwave communications and satellite communications. We can tune these parameters to the requirements of the application. Deploying high gain antennas is another way to reduce the path loss. $$PL(dB)=20log_(dB)\:-(8)$$įrom (8), we can observe that as the transmission power is increased, the path loss is reduced. The path loss is expressed mathematically as We can relate the received power level and the path loss but before that, let’s know the expression of path loss. Like any other gain or attenuation, path loss is also expressed in decibel (dB). The received power level is dependent on factors such as transmission power, antenna gains, frequency of operation and the distance between the transmitter and the receiver. Path loss (PL) refers to the loss or attenuation a propagating electromagnetic signal (or wave) encounters along its path from transmitter to the receiver.Īs a result of path loss, the received signal power level is several orders below the transmitted power level. In this article, we will discuss the path loss and its effects on long distance wireless communications. Some of the common losses taken into consideration during the design of wireless link budgets include atmospheric absorption loss, scattering loss (includes rain attenuation), reflection loss, diffraction loss and path loss. It is important that signal level at the receiver is reasonably above the noise floor so that the detector can faithfully detect and decode the signal data.Īpart from noise, losses in the atmosphere can also distort the transmitted signal. Noise is assumed to get added to the signal and at the receiver we have a signal that carries both the data and the noise.
We often use the AWGN (Additive White Gaussian Noise) model for interpretation of the channel noise. We can’t have a noise-free communication.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
